| Dimension Range(mm) | Plan view size(mm) | Parallelism(mm) | Perpendicularity (mm) |
| 0.5≤L≤10 | ±0.03 | ±0.03 | 0.3 degree for adjacent sides |
| 10≤L≤50 | ±0.05 | ±0.05 | |
| L>50 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 |

Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB), also known as Rare Earth Iron magnet is mainly comsists of iron, neodymium, boron.
It is the strongest permanent magnets currently produced and has excellent magnetic properties, which allow this third generation magnetic material to be compact in size over traditional permanent magnets.
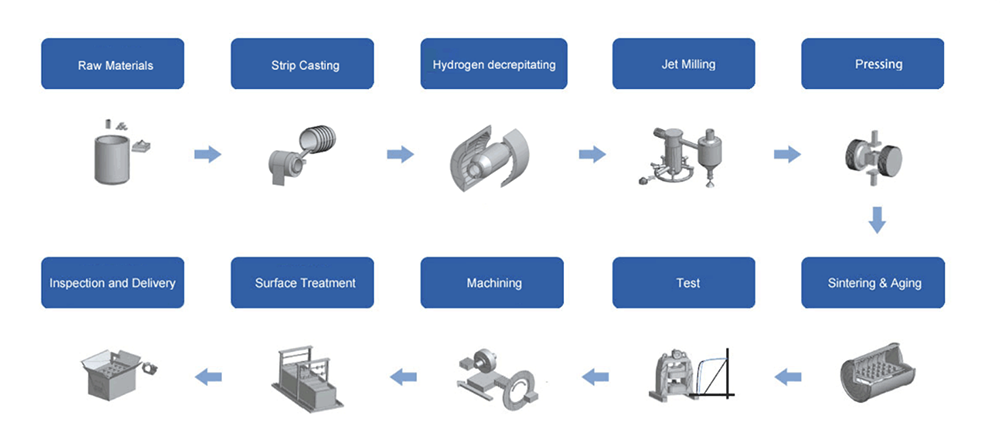
In 1984, Neodymium magnet is discovered, the main phase of Neodumium magnet is Nd2Fe14B and maximum energy products achieved 280kJ/m3 at that time. The successful development of Neodymium magnet announced the birth of the third-generation rare earth permanent magnet. Neodymium magnet is also called NdFeB magnet because they are composed primarily of Neodymium (Nd), Iron (Fe), and Boron (B). Neodymium magnet can be classified to sintered Neodymium magnet, Bonded Neodymium magnet, and hot-pressed Neodymium magnet according to the detailed manufacturing process. Sintered Neodymium magnet is the strongest magnetic and has been widely served to vast kinds of application, include high-performance permanent motors, brushless DC motors, magnetic separators, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), sensors, loudspeakers, consumer electronics, and green energy

Item | Parameters | Reference Value |
Additional magnetic properties | (α(Br))/(%/K) Temp.Coeff.ofBr | -0.08~-0.12 |
(β(Hcj))/(%/K)Temp.Coeff.of Hcj | -0.42~-0.70 | |
(Tc)/(°C)Curie Temperature | 310~380 | |
(μrec)/(-)Recoil Permeability | 1.05 | |
Mechanical and physical properties | (g/cm3) Density | 7.45~7.70 |
(Hv) Vickers Hardness | 650 | |
(μΩ•m)Electrical Resistivity | 1.4 | |
(MPa) Compressive Strength | 1050 | |
(MPa)Tensile Strength | 80 | |
(MPa)Bending Strength | 290 | |
(W/(m•K))Thermal Conductivity | 6~8 | |
(GPa) Young’s Modulus | 160 | |
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion(C ⊥) | -1.5 | |
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion(C //) | 6.5 |
| Dimension Range(mm) | Plan view size(mm) | Parallelism(mm) | Perpendicularity (mm) |
| 0.5≤L≤10 | ±0.03 | ±0.03 | 0.3 degree for adjacent sides |
| 10≤L≤50 | ±0.05 | ±0.05 | |
| L>50 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 |

| Dimension Range(mm) | Cylindricity(mm) | Tolerance(mm) | Parallelism(mm) |
| 1≤D≤5 | ±0.02 | ±0.02 | ±0.02 |
| 5≤D≤25 | ±0.03 | ±0.05 | ±0.03 |
| 25≤D≤50 | ±0.05 | ±0.05 | ±0.05 |
| D>50 | ±0.05 | ±0.1 | ±0.1 |

| Dimension Range(mm) | Cylindricity(mm) | Tolerance(mm) | Parallelism(mm) |
| 1≤d≤3 | ±0.02 | ±0.02 | ±0.02 |
| 3≤d≤5 | ±0.04 | ±0.03 | ±0.02 |
| 5≤d≤15 | ±0.05 | ±0.05 | ±0.03 |
| d>15 | ±0.1 | ±0.05 | ±0.1 |

| Item | Dimension Range(mm) | Tolerance |
| Thickness | T≤10 | ±0.04 |
| 10<T≤25 | ±0.05 | |
| Length | L≤10 | ±0.03 |
| 10< L≤25 | ±0.03 | |
| 25< L≤63 | ±0.04 | |
| L>63 | ±0.06 | |
| Chordal Length | W>63 | ±0.05 |
| W>63 | ±0.06 |

Sintered NdFeB magnet is easy to corrode, coating on the surface would be helpful. Traditional coatings are Phosphating, RB, Zn, NiCuNi, ZnNi and Epoxy with other options available. Selection of a coating should be discussed early on in the design and application process.
>> Temporary: Phosphating, RB
>> Inorganic: White Zn, Coloried Zn, NiCuNi, CuNi, Copper+Nickel, ZnNi
>> Organic: Electrophoresis Epoxy, Spraying Epoxy

